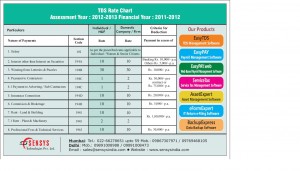
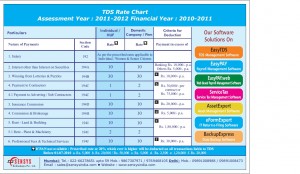
Income Tax Exemptions under various sections : Assessment Year 2013-14
|
Sr No |
Section |
Details of deductions |
Limit |
| 1 | 80C | General deduction for investment in PPF,PF,Life Insurance, ULIP, Stamp duty on house, Fixed deposits for 5 years , bonds etc |
Maximum Rs 1 ,00,000 is allowed. |
| 2 | 80CCC | Deduction in case of contribution to pension fund. However, it should be noted that surrender value or employer contribution is considered income. | Maximum is Rs 1,00,000 |
| 3 | 80CCD | Deduction in respect to contribution to new pension scheme. Employees of central and others are eligible. | Maximum is sum of employer’s and employee’s contribution to the maximum : 10 % of salary. |
| 5 | 80D | Medical insurance on self, spouse , children or parents | Rs 15,000 for self , spouse & children |
| Extra Rs 15,000 for insurance on parents. IF parents are above 65 years, extra sum should be read as Rs 20,000 | |||
| Thus maximum is Rs. 35,000 p.a. | |||
| 6 | 80DD | For maintenance including treatment or insurance of physical disable dependent relatives | Rs 50,000 . In case disability is severe , the amount is Rs 1,00,000. |
| 7 | 80DDB | For medical treatment of self or relatives suffering from specified disease | Acutal amount paid to the extent of Rs 40,000. In case of patient being Sr Citizen , amount is Rs 60,000 |
| 8 | 80E | For interest payment on loan taken for higher studies for self or education of spouse or children | Actual amount paid as interest and start from the financial year in which he /she starts paying interest and runs till the interest is paid in full. |
| 9 | 80G | Donations to charitable institution | 100% or 50% of amount of donation made to 19 entities (National defense fund , Prime minister relief fund etc. ) |
| 10 | 80GG | For rent paid. | This is only for people not getting any House Rent Allowance. Maximum is Rs 2000 per month. Rule 11B is method of computation. |
| 11 | 80GGA | For donation to entities in scientific research or rural development. | Only those tax payers who have no business income can claim this deduction .Maximum is equivalent to 100 % of donation. |